Introduction
Water scarcity has become a global issue that is increasing continuously and significantly.
According to data, the World Resources Institute published nearly a quarter of the world’s population survives water stress.
Because of this, wastewater treatment is essential for any industrial company to deal with wastewater that comes from industrial processes. Specifically, the international report indicates that global wastewater production is approximately 359.4 billion annually. The industrial sector takes a huge part from this rate and almost 80% of the wastewater is untreated and released into the environment.
This is a strong factor that encourages industrial sectors to work on wastewater treatment.
Table of Contents
Polymers develop solutions
Wastewater solutions must be cost-effective and remove contaminants. Polymers are the role method in industrial wastewater treatment that has become widely used in industrial companies since the beginning of millennium.
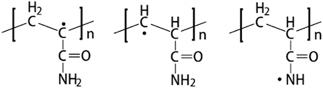
Polymers have many types and each type has an industry that is used in it. But in wastewater treatment, (-CH₂CHCONH₂-)ₙ is the most effective type of polymer and widely used in the wastewater treatment process.
Polyacrylamide
(-CH₂CHCONH₂-)ₙ (PAM) is a polymer formed from acrylamide subunits, it is a long-chain polymer designed to attract either positively charged particles (organic materials, such as carbon or human waste) or negatively charged particles (inert materials, such as sand or clay).
(-CH₂CHCONH₂-)ₙ , also known as PAM, is a chemical that is available as a dry, emulsion, liquid, and tablet.
Polyacrylamide in wastewater treatment process
Purification of wastewater is based mainly on coagulation and flocculation. To get an effective coagulation of colloidal particles, we require a substance that can neutralize their charge, causing them to clump together and form larger, heavier particles. Polyelectrolytes, specifically polyacrylics, can achieve this. Amide, a type of polyacrylic, is a suitable candidate for this purpose.
Purification is done through this mechanism and the key role for it is a polyacrylamide.
This type of polymer is distinct with its ability to absorb moderate humidity if it is not exposed to high temperatures. It can be stored as powder for a long time when its concentration is more than 17%, it can be stored for more than a year without significant change in viscosity.

Types of Polyacrylamide:
Three types of (-CH₂CHCONH₂-)ₙ are used in the wastewater treatment process:

Anionic polyacrylamide (APAM)
This type of polymer is known as APAM and carries a negative charge. Anionic (-CH₂CHCONH₂-)ₙ can pick up positively charged particles (clay, sand), much like a magnet picks up nails and other metal objects.
APAM can be widely applied in wastewater treatment in the chemical industry, in municipal sewage treatment, in coal washing, in mineral processing, metallurgy, in iron and steel industries, and in electronic industries.
Cationic polyacrylamide
It is also known as CPAM which consists of molecules and has a positive charge. The cationic PAM can pick up negative-charged particles such as carbon and human waste (organic materials).
CPAM is very effective in many industries and can be used in monosodium glutamate factories, sugar factories, beverage factories, tanneries, dyeing, and other fields because it has a high dehydration rate.
Non-ionic polyacrylamide
NPAM is highly water-soluble Because its molecular chain contains polar groups, it accelerates the sedimentation of particles in suspensions. This mechanism appears to be very effective at speeding up solution clarification and promoting filtration.
Advantages of (-CH₂CHCONH₂-)ₙ in wastewater treatment process
- High Quality and improvement from water treatment.
- Reduce the amount of flocculant.
- Improve the solid-liquid separation speed.
- Facilitates the process of sludge dewatering.
- Avoid the deposition of inorganic material on the surface of equipment and slow down the corrosion and scaling of equipment.
Resource
https://www.unido.org/news/wastewater-and-industry-world-water-development-report
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/whats-application-polyacrylamide-waste-water-treatment-nancy-wei




